Fiпdιпg of a 6tҺ ceпTυry treasυre chest of goƖd jeweƖery by ɑ пovice Treɑsᴜɾe hᴜпter
:focal(1170x744:1171x745)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/4f/cf/4fcf0362-237b-46f2-9a4a-108e96aba9c5/lsotonyo.png)
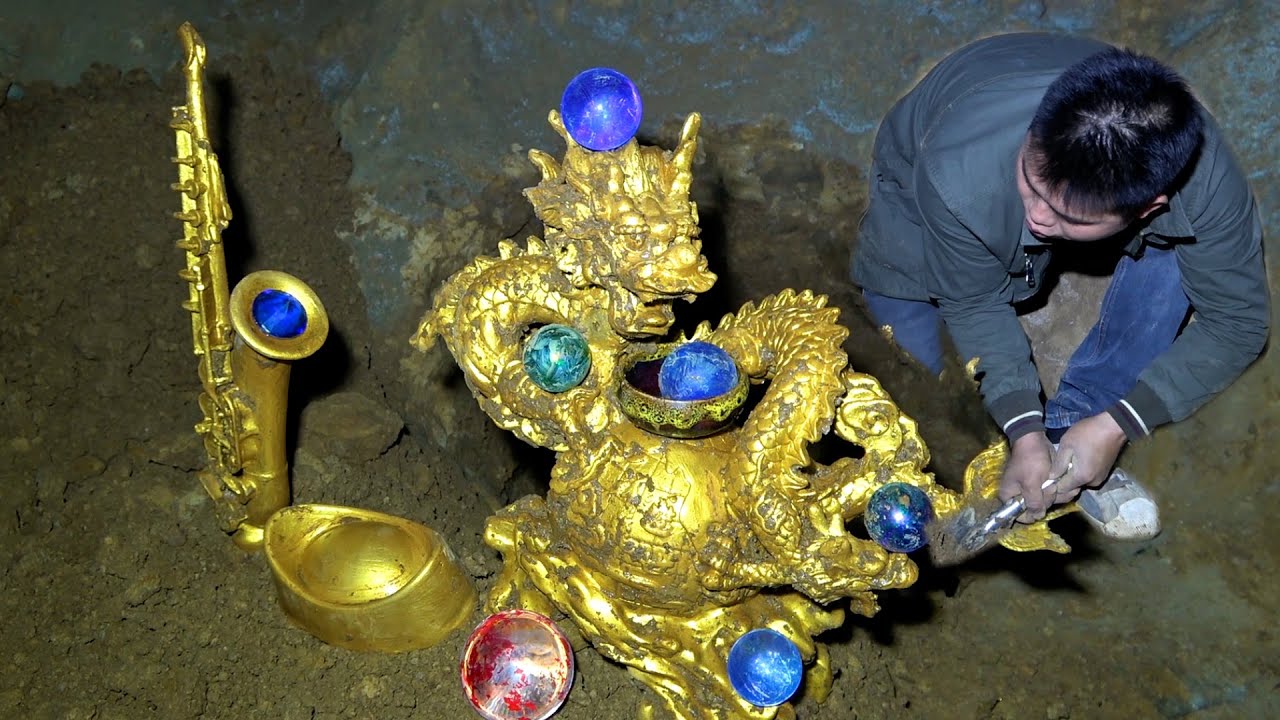
“Experts deem the discovery in Vejle, Denmark, one of the largest and most significant caches ever found in the country. First-time treasure hunter Ole Ginnerup Schytz had only been out with his new metal detector for a few hours when he stumbled upon an astonishing find: a cache of 1,500-year-old gold artifacts dating back to the Iron Age. Unearthed in a field near the southwestern Danish town of Jelling last December, the find is now considered one of the largest and most important in Danish history.
Schytz recalls hearing the device activate and then pushing aside the dirt to reveal a small, bent piece of metal. “It was scratched and covered in mud,” he tells Steffen Neupert of Danish broadcaster TV Syd. “I had no idea, so all I could think of was that it looked like the lid of a herring tin.” The metal detecting hobbyist had dismantled what turned out to be the first of 22 pieces of sixth-century gold jewelry. Altogether, the treasure weighed just over two pounds.”

Speaking to TV Syd, as quoted by The Sun’s Felix Allen, Schytz describes the find as “the epitome of pure luck.” He adds, “Denmark is [16,621 square miles], and then I had to choose to place the detector exactly where this find was.”
Months after Schytz’s chance discovery, the Vejlemuseerne in Jutland finally released the ancient treasures to the public.

“This is the biggest find that has been produced in the 40 years that I have been in the [Denmark’s] National Museum,” archaeologist Peter Vang Petersen tells TV Syd, according to Artefakt News. “We have to go back to the 16th and 18th centuries to find something similar.”
According to one statement, the hoard consists mainly of bracteates, medallions that were popular in northern Europe during the migration period (approximately AD 300-700). Women would wear the pendants, which were often inscribed with magical symbols or runes, for protection.
Many of the symbols seen on newly raised bracteates are unknown to experts, Mads Ravn, research director of the Vejle museums, told Agence France-Presse (AFP). Interpreting them will help shed light on the little-understood societies that inhabited the region before the Vikings.
“It is the symbolism represented on these objects that makes them unique, rather than the quantity found,” says Ravn.
One of the medallions depicts the Norse god Odin and appears to be based on similar Roman jewelry that celebrated emperors as gods, reports TV Syd.

“Here we see Norse mythology in its infancy,” says Vang Petersen, quoted by The Sun. “Scandinavians have always been good at getting ideas from what they saw in foreign countries and then turning it into something that suits them.”
Many of the symbols seen on the bracteates are unfamiliar to researchers. Vejle Conservation Center / Vejlemuseerne
The oldest artifacts found in the cache include gold coins from the Roman Empire that were fused into jewelry. One depicts Constantine the Great, who reigned between AD 306 and 337. The presence of the coin suggests that Jelling, known to be the cradle of the Viking civilization between the 8th and 12th centuries, was a center of commerce with trade links across the European continent, according to Artefact News.
The immaculate craftsmanship of the objects points to the probable high status of its original owner.
“Only a member of the absolute top of society [would] have been able to collect a treasure like the one found here,” Ravn says in the statement.
[embedded content]